In tier 2 and tier 3 cities across India, where sewerage systems are often inadequate, private sanitation solutions such as septic tanks have become increasingly common.
More than 30% of new homes in these regions rely on septic tanks for managing sewage. The effectiveness of these systems heavily depends on the correct sizing of the septic tank. This article explores why septic tank size is crucial, the factors influencing its size, and provides guidance on choosing the right tank for your home.
What Is a Septic Tank?
A septic tank is an underground chamber used for the treatment and disposal of household sewage. It operates by holding sewage long enough for solids to settle out and for bacteria to break down the waste. A standard septic tank consists of two main components:
- The Tank: A sealed compartment where sewage is collected. Solid waste settles at the bottom, forming a sludge layer, while fats and oils float to the top, creating a scum layer. The liquid sewage in the middle exits the tank and moves to the drain field.
- The Drain Field: Also known as the leach field, this is where treated wastewater is dispersed into the soil. The soil acts as a natural filter, removing harmful bacteria and contaminants before the water reenters the groundwater system.
Types of Septic Tanks
Several types of septic tanks are commonly used, each with its advantages and limitations:
- Concrete Septic Tanks: Concrete is a traditional and durable material for septic tanks. These tanks are heavy and require specialized equipment for installation. They are prone to cracking over time if not properly maintained.
- Fiberglass Septic Tanks: Made from lightweight fiberglass, these tanks are easier to transport and install compared to concrete tanks. They are resistant to corrosion but can be more expensive.
- Plastic Septic Tanks: Plastic tanks are another lightweight option that is easy to install. They are resistant to rust and corrosion but may not be as durable as concrete tanks.
Why Is Septic Tank Size Important?
Choosing the right size for a septic tank is essential for maintaining an efficient and trouble-free wastewater management system. Here’s why:
- Prevention of Overflows and Blockages: An undersized septic tank cannot handle the volume of sewage generated by your household. This can lead to frequent overflows, blockages, and unpleasant odors. In extreme cases, it may cause raw sewage to back up into your home.
- Efficient Waste Decomposition: A septic tank that is too small will not provide enough time for the sewage to properly decompose. Solid waste may accumulate faster than it can be broken down, leading to premature tank failures and costly repairs.
- Optimal Bacterial Activity: Bacteria play a crucial role in breaking down waste in the septic tank. If the tank is too large relative to the amount of sewage, there may not be enough organic material to support bacterial growth, which can impair the tank’s effectiveness.
- Cost Efficiency: A tank that is too large may be more expensive and unnecessarily complex. Conversely, an undersized tank may require frequent pumping and maintenance, leading to higher long-term costs.
Factors Determining Septic Tank Size
Several factors influence the appropriate size for a septic tank:
- Water Usage: The amount of water your household uses is a primary factor in determining septic tank size. Larger households with higher water consumption require larger tanks. Here are some general guidelines based on daily water usage:
- Less than 2000 liters per day: 3500-liter tank
- Less than 3000 liters per day: 4600-liter tank
- Less than 3500 liters per day: 6000-liter tank
- Less than 5000 liters per day: 7200-liter tank
- Size of the Property: The size of your home also affects septic tank size. Larger properties with more fixtures will typically need larger tanks. For example:
- Homes less than 1,500 square feet generally require a 3000 to 3800-liter tank.
- Homes around 2,500 square feet may need a tank with a capacity exceeding 4000 liters.
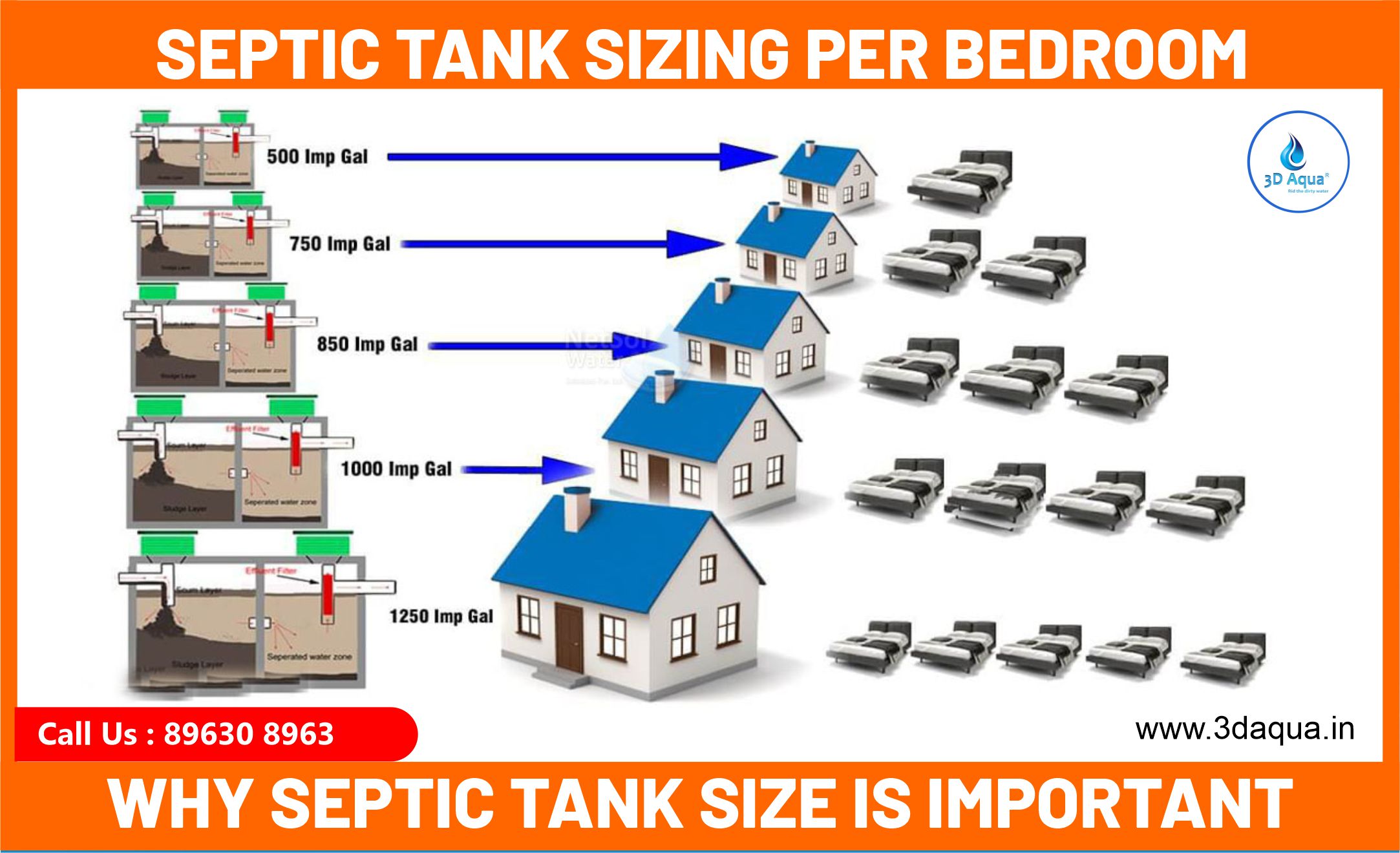
- Number of Bedrooms: The number of bedrooms in a home is a key indicator of household size and water usage. Recommended tank sizes based on the number of bedrooms include:
- A two-bedroom house: 3000-liter tank
- A three-bedroom house: 3800-liter tank
- A four-bedroom house: 4600-liter tank
- A five-bedroom house: 5700-liter tank
- Number of Occupants: The total number of people living in the house directly impacts the septic tank’s required size. More occupants generate more sewage, necessitating a larger tank to handle the increased load.
Empirical Calculations for Sizing a Septic Tank
To determine the precise size of a septic tank, empirical formulas can be used. A common formula for calculating septic tank capacity is:
C=A+P×(rq+ns)C = A + P \times (rq + ns)C=A+P×(rq+ns)
Where:
- C is the capacity of the septic tank.
- A is a constant (e.g., 2000 liters).
- P is the number of users.
- r is the minimum retention time.
- q is the average sewage flow in liters per person per day.
- n is the number of years sludge is stored.
- s is the rate of sludge accumulation in liters per person per year.
In British codes, this formula simplifies to:
C=2000+180PC = 2000 + 180PC=2000+180P
For example, for a household with four users:
C=2000+180×4=2900 litersC = 2000 + 180 \times 4 = 2900 \text{ liters}C=2000+180×4=2900 liters
Thus, a minimum size of 2900 liters is required, with a recommended tank size being approximately 3000 liters for practicality.
Design Considerations
When installing a septic tank, consider the following design parameters:
- Dimensions: For a rectangular septic tank, the length should be 2 to 4 times the width. For a circular tank, the diameter should not be less than 1.35 meters, with a depth of at least 1 meter.
- Minimum Dimensions: The minimum width should be 750 mm (2.5 feet), and the depth should be 1 meter below the outlet. This ensures adequate space for sludge accumulation and effective wastewater treatment.
- Free Space: Maintain 1 to 1.5 feet of free space above the water level inside the tank to allow for expansion and effective waste management.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct size for a septic tank is crucial for efficient wastewater management and maintaining a healthy living environment. By considering factors such as water usage, property size, number of bedrooms, and number of occupants, you can select a tank that meets your household’s needs and ensures reliable performance.
For installation and maintenance of septic tanks and other wastewater treatment solutions, 3D Aqua offers industry-leading expertise. As a top manufacturer of water and wastewater treatment plants, including septic tanks, RO plants, and water softeners, 3D Aqua is known for its quality and customer support. For more information, contact 3D Aqua at +91-8963089630 or email info@3daqua.in.
By understanding and addressing the importance of septic tank sizing, homeowners can avoid common problems and ensure their private sanitation systems operate efficiently and effectively.