In the process of wastewater treatment, the separation of solids from liquids is crucial to improving water quality and ensuring the protection of public health and the environment. Settling tanks—both primary and secondary—play key roles in this mission. These tanks, also known as sedimentation tanks or clarifiers, are designed to allow particles to settle out of water using gravity. Although they perform a similar function in principle, the differences in their design, purpose, and operation significantly impact how effectively wastewater is treated.
In this article, we’ll explore in depth how primary and secondary settling tanks differ in their function, design, and operation—and how manufacturers like 3D Aqua are building advanced wastewater treatment solutions tailored to every industry’s needs.
Understanding Settling Tanks in Wastewater Treatment
Before diving into the distinctions, let’s understand the broader context. Wastewater treatment typically consists of multiple stages: preliminary, primary, secondary, and sometimes tertiary treatment. The goal is to remove contaminants from sewage or industrial effluent and return clean water to nature or reuse it in a safe manner.
Settling tanks come into play in both primary and secondary stages. They allow solids to settle by reducing the flow velocity of wastewater. This settling mechanism separates solids based on their weight and size, enabling further treatment of clarified water and easier handling of sludge.
What Is a Primary Settling Tank?
Function of Primary Settling Tanks
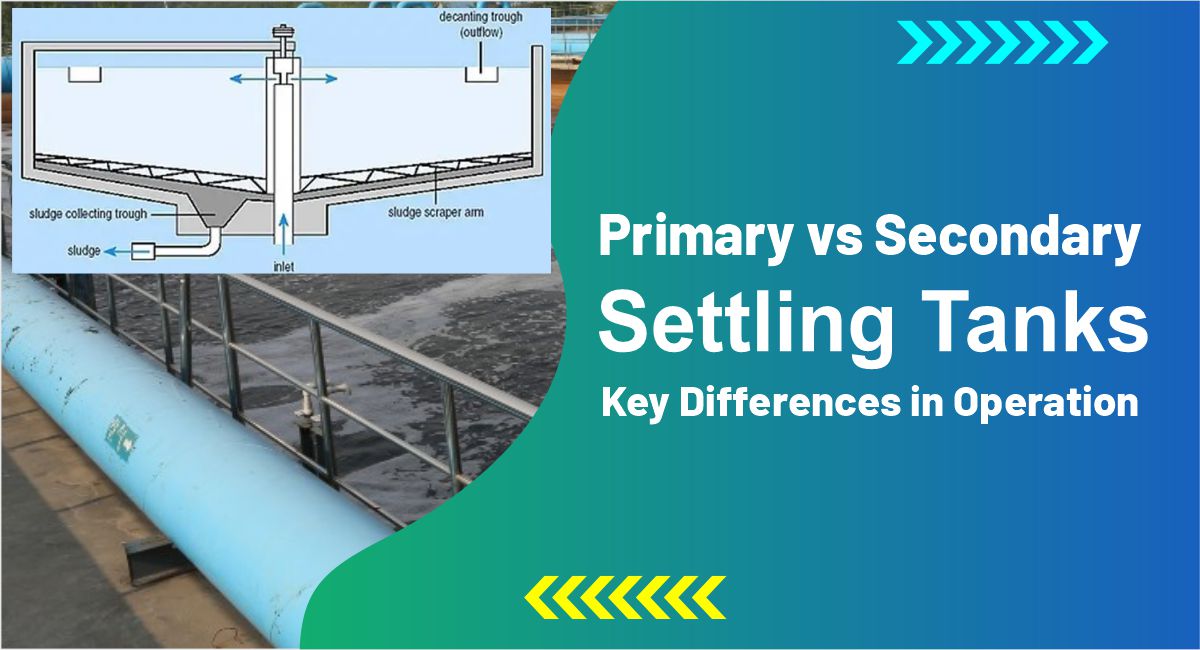
The primary settling tank, also known as the primary clarifier, is used during the primary stage of wastewater treatment. Its function is straightforward: remove settleable solids and floating materials like oils and grease from raw wastewater.
These tanks usually follow screening and grit removal processes, which eliminate large objects and heavier inorganic particles. The water entering the primary tank still contains a significant amount of suspended organic and inorganic solids, and this is where gravity-based separation becomes critical.
How It Works
- Slow Flow Rate: Wastewater enters the tank at a controlled rate to reduce turbulence.
- Sedimentation: Heavier solids settle at the bottom of the tank, forming primary sludge.
- Scum Removal: Lighter materials, such as oils and grease, float to the surface and are removed by mechanical skimmers.
- Effluent Discharge: The clarified water in the middle layer moves to the secondary treatment stage.
Design Aspects
- Rectangular or Circular Tanks: These tanks may be rectangular with a horizontal flow or circular with a radial flow.
- Inlet Zone: Designed to evenly distribute flow and reduce turbulence.
- Outlet Zone: Equipped with weirs to allow uniform flow of clarified water.
- Sludge Collection Mechanism: Scrapers or pumps remove sludge from the bottom.
Purpose and Benefits
- Reduces Load: Removes 50-70% of suspended solids and 30-40% of BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand), making secondary treatment more efficient.
- Cost-Efficient: Reduces chemical demand and operational load on downstream processes.
- Prepares for Biological Treatment: By eliminating heavy solids early, biological processes in the secondary stage can focus on finer particles and dissolved pollutants.
What Is a Secondary Settling Tank?
Function of Secondary Settling Tanks
The secondary settling tank, also known as the secondary clarifier, is part of the secondary treatment phase. Its primary job is to separate biological floc (activated sludge) formed during the biological treatment stage from treated water.
After wastewater undergoes biological treatment—usually in an aeration basin or trickling filter—it carries a high concentration of microbial biomass. These microbes, now clustered together as flocs, must be removed before discharging or further processing.
How It Works
- Influent Introduction: Water from the aeration tank enters the clarifier at a steady flow.
- Gravity Separation: Flocculated solids (activated sludge) settle at the bottom, forming secondary sludge.
- Effluent Collection: Clear water at the top flows over weirs into effluent channels.
- Sludge Recycling: A portion of settled sludge is recycled back into the aeration tank to maintain microbial population. The excess sludge is sent for further treatment or disposal.
Design Aspects
- Deeper and Larger Tanks: These tanks are often deeper than primary clarifiers to allow fine particles more time to settle.
- Sludge Return Systems: Includes mechanisms like return activated sludge (RAS) and waste activated sludge (WAS) lines.
- Inlet Structures: Designed to minimize turbulence and flow short-circuiting.
- Sludge Hoppers and Scrapers: Move collected sludge to the central pit for extraction.
Purpose and Benefits
- Removes Biological Solids: Eliminates 85-95% of remaining solids from biological treatment.
- Improves Clarity: Produces nearly clear water ready for disinfection or tertiary treatment.
- Supports Reuse: Helps meet environmental standards for water reuse or discharge.
- Enhances Efficiency: Enables efficient biomass management in the treatment cycle.
Key Differences Between Primary and Secondary Settling Tanks
| Feature | Primary Settling Tank | Secondary Settling Tank |
|---|---|---|
| Stage | Primary treatment | Secondary treatment |
| Purpose | Remove heavy organic/inorganic solids | Remove biological solids (activated sludge) |
| Effluent Source | Raw sewage after screening | Aeration tank or biological treatment |
| Sludge Type | Raw primary sludge | Biological secondary sludge |
| Design Depth | Shallow to medium | Deeper to allow finer settling |
| Flow Control | Simple inlets/outlets | Advanced flow and sludge recycling systems |
| Removal Efficiency | 50-70% of suspended solids | 85-95% of remaining solids |
| Odor Potential | Higher due to untreated waste | Lower as waste is biologically processed |
Importance of Both Tanks in Wastewater Treatment
Though they serve different purposes, both tanks are indispensable:
- Primary tanks reduce the initial load, protecting downstream equipment and saving costs.
- Secondary tanks polish the effluent, ensuring high-quality discharge that meets legal and environmental standards.
Neglecting either stage can result in overburdened biological systems, incomplete treatment, environmental harm, and regulatory violations.
Innovations by 3D Aqua in Settling Tank Design
At 3D Aqua, we understand that effective sedimentation forms the backbone of any wastewater treatment plant. That’s why our custom-designed primary and secondary clarifiers are engineered for durability, efficiency, and cost savings.
Our Key Features:
- Customized Designs: Tailored tank size, material, and shape based on your site’s requirements.
- Energy-Efficient Systems: Gravity-based flow and mechanical scrapers reduce energy use.
- Minimal Maintenance: Corrosion-resistant materials and self-cleaning designs.
- Smart Automation: Optional IoT-based monitoring for flow rates, sludge levels, and performance.
- All-in-One Solutions: Integrated with screens, aerators, and sludge treatment for seamless operations.
Applications We Serve:
- Municipal Sewage Systems
- Industrial Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs)
- Residential and Commercial Complexes
- Food, Beverage, Textile, Pharma, and Chemical Industries
Whether you need a clarifier for a 100 KLD or 10 MLD plant, we provide turnkey solutions that scale to your demands.
Conclusion
The role of primary and secondary settling tanks in wastewater treatment cannot be overstated. Each tank serves a specific function—removing solids at different stages—and together, they ensure that treated water is safe, clear, and reusable. From simple gravity sedimentation in primary tanks to controlled biological separation in secondary tanks, these components are crucial in ensuring smooth operations and regulatory compliance.
Choosing the right system means choosing a partner that understands water. At 3D Aqua, we design settling tanks and complete wastewater treatment systems that work efficiently, are easy to maintain, and provide reliable results.
Contact 3D Aqua Today
Let us help you design a robust water treatment system with high-performance clarifiers and cutting-edge components tailored to your needs.
📞 Phone: +91-6262629090
📧 Email: info@3daqua.in
🌐 Website: www.3daqua.in
We offer complete solutions for ETP, STP, RO Plants, and more across India. Whether you’re in Raipur, Gurgaon, Noida, Meerut, or any other region, we’re just a call away.