Waste management refers to the systematic process of collecting, treating, and disposing of waste materials in a safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible manner. This multifaceted discipline encompasses a wide array of activities including garbage collection, recycling, composting, landfill management, and energy recovery. The ultimate goal of waste management is to minimize the adverse effects of waste on human health and the environment, ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.
In an age marked by rapid urbanization, industrialization, and consumerism, the significance of effective waste management has never been more pronounced. As populations grow and lifestyles change, the volume of waste produced increases dramatically, necessitating robust waste management strategies. This article delves into the importance of waste management, exploring its benefits across various domains—environmental protection, resource conservation, energy savings, health and safety, economic advantages, regulatory compliance, and the promotion of a circular economy.
You may like this also: What is Solid Waste Management? Types, Methods, Effects, and Importance
The Importance of Waste Management
1. Environmental Protection

One of the most critical functions of waste management is the protection of our environment. Improper waste disposal can lead to significant pollution of air, water, and soil. Landfills overflowing with waste can emit harmful substances, while incineration can release toxic fumes into the atmosphere. Effective waste management practices minimize these risks.
By implementing systematic waste collection and treatment, harmful pollutants are kept in check. This not only protects ecosystems but also ensures that wildlife and human populations are shielded from the adverse effects of pollution. For instance, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills can help prevent the leaching of hazardous materials into groundwater, which can contaminate drinking water sources.
Furthermore, proper waste management contributes to the preservation of natural habitats. By reducing the amount of waste generated and promoting recycling, we can minimize the destruction of forests and other ecosystems that would otherwise be exploited for raw materials.
2. Resource Conservation

Another vital aspect of waste management is resource conservation. The recycling and reusing of materials significantly decrease the demand for new raw materials. For instance, recycling paper reduces the need for deforestation, while recycling metals diminishes the necessity for mining.
This conservation of resources is essential for several reasons. First, it leads to a more sustainable approach to production and consumption. By reusing materials, we reduce the environmental footprint associated with extracting, processing, and transporting new raw materials.
Second, resource conservation also translates into energy savings. The processes involved in extracting and refining raw materials are often energy-intensive. By recycling, we can significantly cut down on energy consumption, which in turn helps combat climate change.
3. Energy Savings

Waste management practices, particularly recycling and waste-to-energy technologies, can contribute to energy savings. Recycling materials such as aluminum, glass, and plastics often require less energy compared to producing these materials from scratch. For example, recycling aluminum saves about 95% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum from bauxite ore.
Additionally, waste-to-energy facilities convert non-recyclable waste materials into usable energy, often in the form of electricity or heat. This process not only helps reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills but also provides a renewable energy source that can help meet energy demands and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
By harnessing the energy contained in waste, we can move towards a more sustainable energy future, reducing our carbon footprint and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
4. Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions

Improper waste management practices contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane, which is released from landfills. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that has a much greater warming potential than carbon dioxide over a short period. Effective waste management strategies, including recycling and composting, can substantially reduce methane emissions.
When organic waste is sent to landfills, it decomposes anaerobically (without oxygen), producing methane. However, composting organic waste allows it to decompose aerobically (with oxygen), significantly reducing methane production. By diverting organic waste from landfills through composting and other organic recycling methods, we can mitigate the effects of climate change.
Furthermore, recycling reduces the need for energy-intensive production processes that generate greenhouse gases. For instance, recycling plastic not only conserves petroleum resources but also lowers emissions associated with its production.
5. Health and Safety

Waste management is critical to public health and safety. Improper waste disposal can lead to a range of health hazards, including disease transmission, water contamination, and air pollution. Waste that is not managed correctly can become breeding grounds for pests and pathogens, leading to outbreaks of diseases such as cholera and malaria.
Effective waste management minimizes these health risks by ensuring that waste is collected, treated, and disposed of properly. This not only protects communities but also safeguards workers in the waste management industry. Implementing safety protocols and regulations ensures that workers are not exposed to hazardous materials or unsafe working conditions.
By prioritizing health and safety in waste management practices, we create a healthier environment for all members of the community.
6. Aesthetic Improvement

The aesthetic quality of our surroundings plays a significant role in our overall quality of life. Poor waste management can lead to littered streets, polluted landscapes, and unsightly landfills. Conversely, effective waste management contributes to cleaner, more attractive communities.
Proper waste disposal practices enhance the visual appeal of neighborhoods and public spaces. This, in turn, fosters a sense of pride among residents and encourages community engagement. Cleaner environments are also more likely to attract tourists, boosting local economies.
Moreover, aesthetically pleasing surroundings have been linked to improved mental well-being. Access to clean, green spaces and well-maintained public areas can have a positive impact on the physical and mental health of individuals.
7. Economic Benefits

Waste management is not only beneficial for the environment and public health; it also has significant economic advantages. The waste management sector creates job opportunities in various fields, including recycling, waste collection, processing, and environmental consulting.
As communities invest in sustainable waste management practices, they can stimulate local economies and foster innovation. The development of new technologies and systems for waste processing can lead to further job creation and economic growth.
Additionally, effective waste management can reduce costs associated with waste cleanup, disposal, and environmental remediation. By minimizing the volume of waste produced and maximizing recycling efforts, municipalities can lower their waste management expenses and allocate resources to other community needs.
8. Compliance with Regulations

Many countries and regions have established strict regulations and guidelines for waste management to protect the environment and public health. Proper waste management practices ensure compliance with these regulations, helping organizations and municipalities avoid legal and financial penalties.
Failing to adhere to waste management regulations can result in costly fines, legal disputes, and damage to a community’s reputation. By implementing effective waste management systems, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship and public health, fostering trust and support from the community.
Furthermore, compliance with waste management regulations often requires ongoing monitoring and reporting, which can lead to improved practices and more efficient resource use.
9. Sustainable Development

Waste management plays a vital role in achieving sustainable development goals. By integrating waste management into broader sustainability initiatives, communities can ensure that they meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Sustainable waste management practices contribute to resource preservation, environmental protection, and social equity. They promote responsible consumption and production patterns, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and waste is minimized.
Moreover, effective waste management is a key component of circular economy principles. By designing products for durability, reparability, and recyclability, we can create a system that values resources and minimizes waste.
10. Promotion of Circular Economy
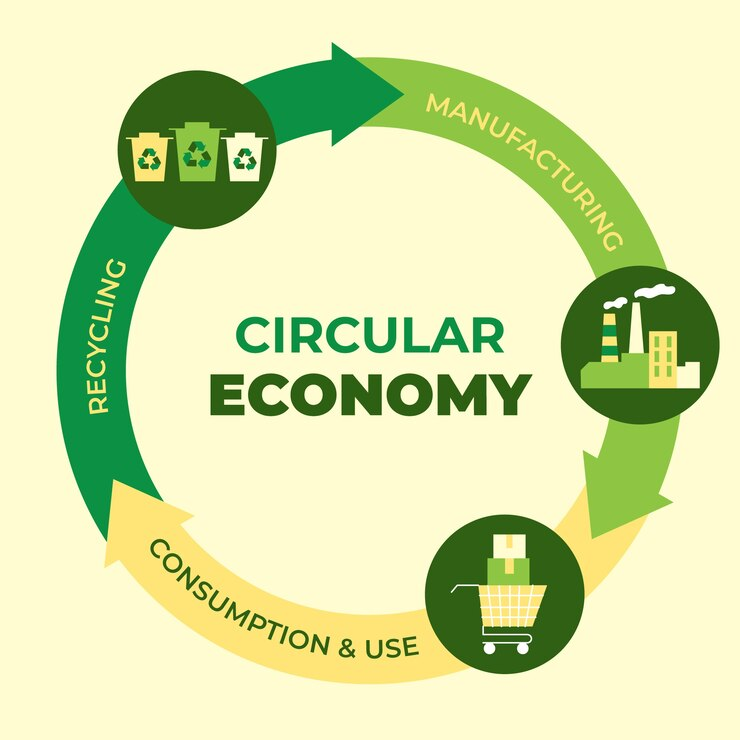
The concept of a circular economy revolves around the idea of closing the loop in resource use. It emphasizes the importance of designing products that can be reused, repaired, or recycled, thereby minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact.
Waste management is a crucial component of the circular economy. By implementing effective recycling programs and promoting sustainable practices, communities can transition from a linear “take-make-dispose” model to a circular approach that values resources and minimizes waste.
This transition not only conserves natural resources but also fosters innovation and economic growth. It encourages the development of new technologies and business models that prioritize sustainability, ultimately leading to a more resilient and sustainable economy.
Conclusion
The importance of waste management cannot be overstated. It plays a crucial role in protecting the environment, conserving resources, promoting public health, and driving economic growth. By adopting effective waste management practices, we can reduce pollution levels, mitigate health risks, and create cleaner, more sustainable communities.
In a world increasingly challenged by the effects of climate change, resource depletion, and urbanization, the need for robust waste management systems is more critical than ever. As individuals, communities, and organizations, we must prioritize waste management and embrace sustainable practices that will ensure a cleaner, healthier future for generations to come. Through collective action and commitment to responsible waste management, we can foster a circular economy that values resources, protects the environment, and promotes social equity.
FAQs
1. What is waste management?
Waste management involves collecting, treating, and disposing of waste materials responsibly to minimize their impact on the environment and public health.
2. Why is waste management important for the environment?
It prevents pollution, conserves natural resources, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and protects ecosystems and wildlife.
3. How does waste management contribute to public health?
Proper waste disposal reduces the risk of disease transmission, water contamination, and air pollution, ensuring healthier communities.
4. What are the economic benefits of waste management?
Waste management creates jobs, lowers cleanup costs, and fosters innovation and economic growth through sustainable practices.
5. How does recycling fit into waste management?
Recycling conserves resources, reduces energy consumption, and minimizes landfill waste, making it a key component of effective waste management.
6. What role does waste management play in sustainable development?
It supports responsible consumption and production patterns, ensuring resources are preserved for future generations while protecting the environment.

